Learn More
Lamin A/C Mouse, Unlabeled, Clone: 14, BD
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Brand: BD Biosciences 612162
Description
The nuclear envelope (NE) is a specialized extension of the ER that contains numerous pore complexes interconnected with the nuclear lamina. The nuclear lamina composes the structural framework for the NE and serves as a chromatin anchor site, thus playing a major role in interphase nuclear organization. The major component of nuclear lamina are intermediate filament-like proteins called lamins. In mammalian somatic cells, there are three major lamins, A, B1, and C, and two minor lamins, B2 and A10. A-type lamins (A, A10, and C) are encoded by a
single gene and are produced by alternative splicing, while B-type lamins (B1 and B2) are encoded by separate genes. B-type lamins are found in all nucleated somatic cells, while the expression of A-type lamins are developmentally regulated. Mice lacking lamin A show no overt abnormalities until postnatal development when perturbations in nuclear envelop structure correlate with the appearance of muscular dystrophy. In addition, lamin A is mutated in lipodystrophy, a disorder characterized by reduction in subcutaneous adipose tissue. Thus, lamin A and C may be important for nuclear envelope formation during postnatal cell differentiation.
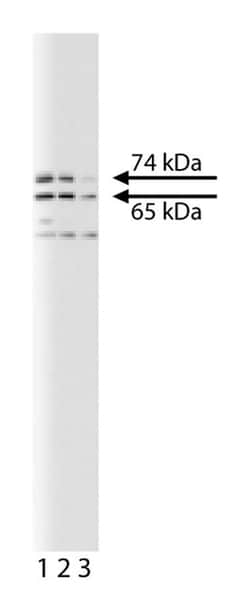
Immunofluorescence, Western Blotting

Specifications
| Lamin A/C | |
| Monoclonal | |
| 250μg/mL | |
| Aqueous buffered solution containing BSA, glycerol, and ≤0.09% sodium azide. | |
| Human Lamin A/C aa. 398-490 | |
| 50 μg | |
| Cell Biology | |
| Canine, Chicken, Human, Mouse, Rat | |
| IgG1 |
| Western Blot | |
| 14 | |
| Unconjugated | |
| Mouse | |
| Affinity Purified | |
| RUO | |
| Primary | |
| Store undiluted at -20°C. |
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.
For Research Use Only.