Learn More
Invitrogen™ CD56 (NCAM) Monoclonal Antibody (TULY56), NovaFluor™ Red 710, eBioscience™
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Brand: Invitrogen™ H013T03R04-A
Description
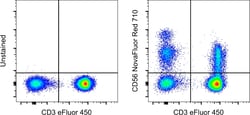
Description: This TULY56 monoclonal antibody reacts with human CD56, also known as Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule (NCAM). Staining with TULY56 does not block binding of CMSSB, suggesting that the two antibodies recognize different epitopes. Additionally, TULY56 performs better after fixation and permeabilization than CMSSB. This product contains 1 vial of NovaFluor conjugate and 1 vial of CellBlox Plus Blocking Buffer. Applications Tested: This TULY56 antibody has been pre-titrated and tested by flow cytometric analysis of normal human peripheral blood cells. This can be used at 5 μL (0.4 μg) per test. A test is defined as the amount (μg) of antibody that will stain a cell sample in a final volume of 100 μL. Cell number should be determined empirically but can range from 10^5 to 10^8 cells/test Master mixes. Whole Blood compatibility: When utilizing whole blood (as opposed to density-gradient-purified PBMC), we recommend lysing red blood cells in bulk prior to staining with NovaFluor conjugates.
CD56, also known as neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM), is a highly glycosylated transmembrane glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin family. It plays a crucial role in cell adhesion, migration, axonal growth, pathfinding, and synaptic plasticity. CD56 is ubiquitously expressed in the nervous system in isoforms ranging from 120-180 kDa and is involved in homotypic adhesion of neural cells. It mediates interactions by binding extracellular matrix components such as laminin and integrins, with polysialic modification reducing CD56-mediated adhesion. In the hematopoietic system, CD56 is expressed on natural killer (NK) cells and a subset of T cells known as NKT cells. It is also found on most neuroectodermal-derived cell lines, tissues, and neoplasms, including retinoblastoma, medulloblastoma, astrocytomas, and neuroblastoma. CD56 serves as a widely used neuroendocrine marker with high sensitivity for neuroendocrine tumors and ovarian granulosa cell tumors. Diseases associated with CD56 dysfunction include rabies and blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasms, highlighting its importance in both neural and immune system functions.
Specifications
| CD56 (NCAM) | |
| Monoclonal | |
| 0.4 μg/Test | |
| PBS with BSA and 0.09% sodium azide; pH 7.2 | |
| P13591 | |
| Ncam1 | |
| Affinity chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 4684, 693789 | |
| 4°C, store in dark, DO NOT FREEZE! | |
| Liquid |
| Flow Cytometry | |
| TULY56 | |
| NovaFluor Red 710 | |
| Ncam1 | |
| adhesion molecule; antigen recognized by monoclonal antibody 5.1H11; Cd56; CD-56; CD56 120 kDa GPI-linked isoform; CD56 140 kDa isoform; CD56 140 kDa VASE isoform; E NCAM; E-NCAM; MSK39; N CAM1; NCAM; N-CAM; Ncam1; N-CAM-1; NCAM-1; NCAMC; NCAM-C; neural cell adhesion molecule; Neural cell adhesion molecule 1; neural cell adhesion molecule, NCAM; sCD56; sNCAM; soluble CD56; soluble NCAM | |
| Mouse | |
| 100 Tests | |
| Primary | |
| Human, Monkey, Rhesus Macaque | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG1 κ |
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.